Abstract
Short Communication
Nanotherapeutic agent for cancer: Miracle or catastrophe
Archna Dhasmana*
Published: 28 June, 2019 | Volume 3 - Issue 1 | Pages: 010-012
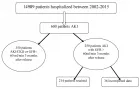
Nanotechnology is a smart technology in the field of biomedical engineering used for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Nanodrugs provide better encapsulation of drug and efficiency at low dosage to kill the targeted tissue/cells. However, the chances of chronic toxicity and high cost of treatment limits its applicability [1]. To overcome these problems still, the experts of the scientific community have been working on it, to design the best one and cost-effective treatment for the human welfare.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001005 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
References
- Huang YW, Cambre M, Lee HJ. The toxicity of nanoparticles depends on multiple molecular and physicochemical mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2017; 18: 2702. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2X6tA8B
- Kim KY. Nanotechnology platforms and physiological challenges for cancer therapeutics. In Nano medicine in Cancer. 2017; 3: 27-46. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2LlLima
- Wang Y, Yu L, Monopoli MP, Sandin P, Mahon E, et al. Nanomedicine: nanotechnology. Biol Med. 2015; 11: 313-327.
- Pippa N, Demetzos C, Pispas S, editors. Drug Delivery Nanosystems: From Bioinspiration and Biomimetics to Clinical Applications. CRC Press; 2019. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2ZUdbWM
- Wei T, Chen C, Liu J, Liu C, Posocco P, et al. Anticancer drug nanomicelles formed by self-assembling amphiphilic dendrimer to combat cancer drug resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015; 112: 2978-2983. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2xjDt8l
- Karlsson J, Vaughan HJ, Green JJ. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles for therapeutic cancer treatments. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2018; 7; 9: 105-127. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2FBHNoc
- Zhang P, Wang J, Chen H, Zhao L, Chen B, et al. Tumor Microenvironment-Responsive Ultrasmall Nanodrug Generators with Enhanced Tumor Delivery and Penetration. J Am Chem Soc. 2018; 140: 14980-14989. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2xkcVDW
- Liu T, Zeng L, Jiang W, Fu Y, Zheng W, et al. Rational design of cancer-targeted selenium nanoparticles to antagonize multidrug resistance in cancer cells. Nanomedicine. 2015; 11: 947-958. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2YhSSCb
- Song J, Lin C, Yang X, Xie Y, Hu P, et al. Mitochondrial targeting nanodrugs self-assembled from 9-O-octadecyl substituted berberine derivative for cancer treatment by inducing mitochondrial apoptosis pathways. J Control Release. 2019; 294: 27-42. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2YryVso
- Greenstein JP. Biochemistry of cancer. Elsevier. 2016; Ref.: http://bit.ly/2YkPUNg
- Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, Stein K, Mariotto A, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012; 62: 220-241. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2NdHHcn
- Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Kramer JL, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016. 2016; 66: 271-289. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2XyLTaR
- Schumacher TN, Schreiber RD. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science. 2015; 348: 69-74. Ref.: http://bit.ly/31XS47H
- Ahles TA, Root JC. Cognitive effects of cancer and cancer treatments. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2018; 14: 425-451. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2IRsMka
- Heath JR, Davis ME. Nanotechnology and cancer. Annu Rev Med. 2008; 59: 251-265. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2xjDM2Z
- Wang X, Yang L, Chen Z, Shin DM. Application of nanotechnology in cancer therapy and imaging. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008; 58: 97-110. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2YhI1Id
- Shi J, Kantoff PW, Wooster R, Farokhzad OC. Cancer nanomedicine: progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017; 17: 20. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2X30XZT
- Jain RK. The next frontier of molecular medicine: delivery of therapeutics. Nature medicine. 1998 Jun;4(6):655., Allen TM. Ligand-targeted therapeutics in anticancer therapy. Nat Med. 2002; 2: 750. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2ZRvpbb
- Nakamura Y, Mochida A, Choyke PL, Kobayashi H. Nanodrug delivery: is the enhanced permeability and retention effect sufficient for curing cancer? Bioconjug Chem. 2016; 27: 2225-2238. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2XGLSl0
- Chen Q, Liang C, Wang C, Liu Z. An imagable and photothermal “Abraxane‐like” nanodrug for combination cancer therapy to treat subcutaneous and metastatic breast tumours. Adv Mater. 2015; 27: 903-910. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2J8EXb8
- Fan W, Yung B, Huang P, Chen X. Nanotechnology for multimodal synergistic cancer therapy. Chem Rev. 2017; 117: 13566-13638. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2Yi9rOr
- Sinha R, Kim GJ, Nie S, Shin DM. Nanotechnology in cancer therapeutics: bio conjugated nanoparticles for drug delivery. Molecular cancer therapeutics. 2006; 5: 1909-1917. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2IS8J54
- Olov N, Bagheri‐Khoulenjani S, Mirzadeh H. Combinational drug delivery using nanocarriers for breast cancer treatments: A review. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018; 106: 2272-2283. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2Nijbaj
- Raza A, Rasheed T, Nabeel F, Hayat U, Bilal M, et al. Endogenous and Exogenous Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems for Programmed Site-Specific Release. Molecules. 2019; 24: 1117. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2XflIX6
- Alexis F, Rhee JW, Richie JP, Radovic-Moreno AF, Langer R, et al. New frontiers in nanotechnology for cancer treatment. Urol Oncol. 2008; 26: 74-85. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2xgI3Ev
- Ferrari M. Cancer nanotechnology: opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005; 5: 161-171. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2Lqemcv
- van Elk M, Murphy BP, Eufrasio-da-Silva T, O’Reilly DP, Vermonden T, et al. Nanomedicines for advanced cancer treatments: Transitioning towards responsive systems. Int J Pharm. 2016; 515: 132-164. Ref.: http://bit.ly/2ZUbxV2
- Qin SY, Zhang AQ, Cheng SX, Rong L, Zhang XZ. Drug self-delivery systems for cancer therapy. Biomaterials. 2017; 112: 234-247. Ref.: http://bit.ly/3021xt1
Figures:
Similar Articles
-
Heat transfer investigation of Non-Newtonian Fluid between two vertically infinite flat plates by numerical and analytical solutionsPourmehran O*,Rahimi-Gorji M,Tavana M,Gorji-Bandpy M,Ganji DD. Heat transfer investigation of Non-Newtonian Fluid between two vertically infinite flat plates by numerical and analytical solutions. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hbse.1001001; 1: 001-011
-
Wifi and health: Perspectives and risksMyriam Ben Salah*,Hafedh Abdelmelek,Manef Abderraba. Wifi and health: Perspectives and risks. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hbse.1001002; 2: 012-022
-
Naphazoline nitrate treat the Frey effect of microwave and other sonic weapon’s damages in Human’s Internal, Endogenous OrgansRobert Skopec*. Naphazoline nitrate treat the Frey effect of microwave and other sonic weapon’s damages in Human’s Internal, Endogenous Organs. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001004; 3: 001-009
-
Nanotherapeutic agent for cancer: Miracle or catastropheArchna Dhasmana*. Nanotherapeutic agent for cancer: Miracle or catastrophe. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001005; 3: 010-012
-
Synthesis of NaYF4:Yb,Er@SiO2@Ag core-shell nanoparticles for plasmon-enhanced upconversion luminescence in bio-applicationsGrigory Arzumanyan*,Dmitriy Linnik,Kahramon Mamatkulov,Maria Vorobyeva,Anastasia Korsun,Valentina Glasunova,Anka Jevremović. Synthesis of NaYF4:Yb,Er@SiO2@Ag core-shell nanoparticles for plasmon-enhanced upconversion luminescence in bio-applications. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001006; 3: 013-019
-
Peptide-based antifouling aptasensor for cardiac troponin I detection by surface plasmon resonance applied in medium sized Myocardial InfarctionJen-Tsai Liu*,Yi Wu,Jia Xin Che,Shwu Jen Chang,Ching-Jung Chen*. Peptide-based antifouling aptasensor for cardiac troponin I detection by surface plasmon resonance applied in medium sized Myocardial Infarction. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001007; 4: 001-008
-
Mesoscopic irreversible thermodynamics of morphological evolution kinetics of helical conformation in bioproteins ‘DNA’ under the isothermal isobaric conditionsTarik Omer Ogurtani*,Ersin Emre Oren. Mesoscopic irreversible thermodynamics of morphological evolution kinetics of helical conformation in bioproteins ‘DNA’ under the isothermal isobaric conditions. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001008; 4: 009-019
-
The Trans-zoonotic Virome interface: Measures to balance, control and treat epidemicsVinod Nikhra*. The Trans-zoonotic Virome interface: Measures to balance, control and treat epidemics. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001009; 4: 020-027
-
C3D data based on 2-dimensional images from video cameraAli Sharifnezhad*,Mina Abdollahzadekan,Mehdi Shafieian,Iman Sahafnejad-Mohammadi. C3D data based on 2-dimensional images from video camera. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001010; 5: 001-005
-
Fecal storage condition induces variations of microbial composition and differential interpretation of metagenomic analysisHansoo Park*,Gihyeon Kim†,Kyoung Wan Yoon†, Changho Park†,Kyu Hyuck Kang,Sujeong Kim,Youngmin Yoon,Sang Eun Lee,Yeongmin Kim. Fecal storage condition induces variations of microbial composition and differential interpretation of metagenomic analysis. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001011; 5: 006-012
Recently Viewed
-
COPD and low plasma vitamin D levels: Correlation or causality?Luca Gallelli*, Erika Cione,Stefania Zampogna, Gino Scalone. COPD and low plasma vitamin D levels: Correlation or causality? . J Pulmonol Respir Res. 2018: doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001008; 2: 011-012
-
Environmental Factors Affecting the Concentration of DNA in Blood and Saliva Stains: A ReviewDivya Khorwal*, GK Mathur, Umema Ahmed, SS Daga. Environmental Factors Affecting the Concentration of DNA in Blood and Saliva Stains: A Review. J Forensic Sci Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001057; 8: 009-015
-
Markov Chains of Molecular Processes of Biochemical MaterialsOrchidea Maria Lecian*. Markov Chains of Molecular Processes of Biochemical Materials. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001076; 7: 001-005
-
Generation of Curved Spacetime in Quantum FieldSarfraj Khan*. Generation of Curved Spacetime in Quantum Field. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001077; 7: 006-009
-
Optimizing Milk Safety: Applying Nuclear Techniques in X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy for Heavy Metal Quantification in Powdered Milk Consumed in SenegalPapa Macoumba Faye*, Djicknack Dione, Oumar Ndiaye, Moussa Hamady SY, Nogaye Ndiaye, Alassane Traore, Ababacar Sadikhe Ndao. Optimizing Milk Safety: Applying Nuclear Techniques in X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy for Heavy Metal Quantification in Powdered Milk Consumed in Senegal. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001078; 7: 010-015
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."